RefractiveIndex.Info interface
Access to the RefractiveIndex.INFO database is provided by the rindexinfo module. A major function of this module is to create glass instances (RIIMedium or InterpolatedMedium) for use in optical models.
from opticalglass import rindexinfo
from opticalglass.rindexinfo import summary_plots
Typical use scenario - Polycarbonate
Ofttimes, a Google search of a “refractive index for Polycarbonate” will include a RefractiveIndex.Info link in the query. Follow the link to the page on RefractiveIndex.INFO for Polycarbonate.
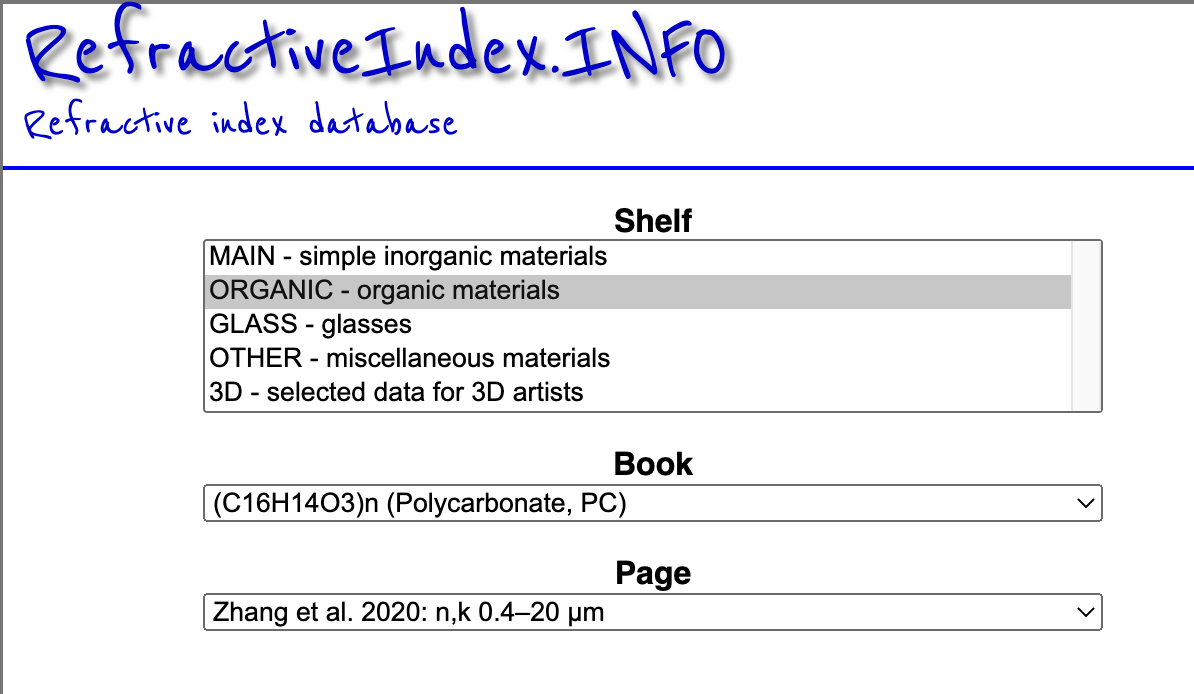
The data is below this on the web page.
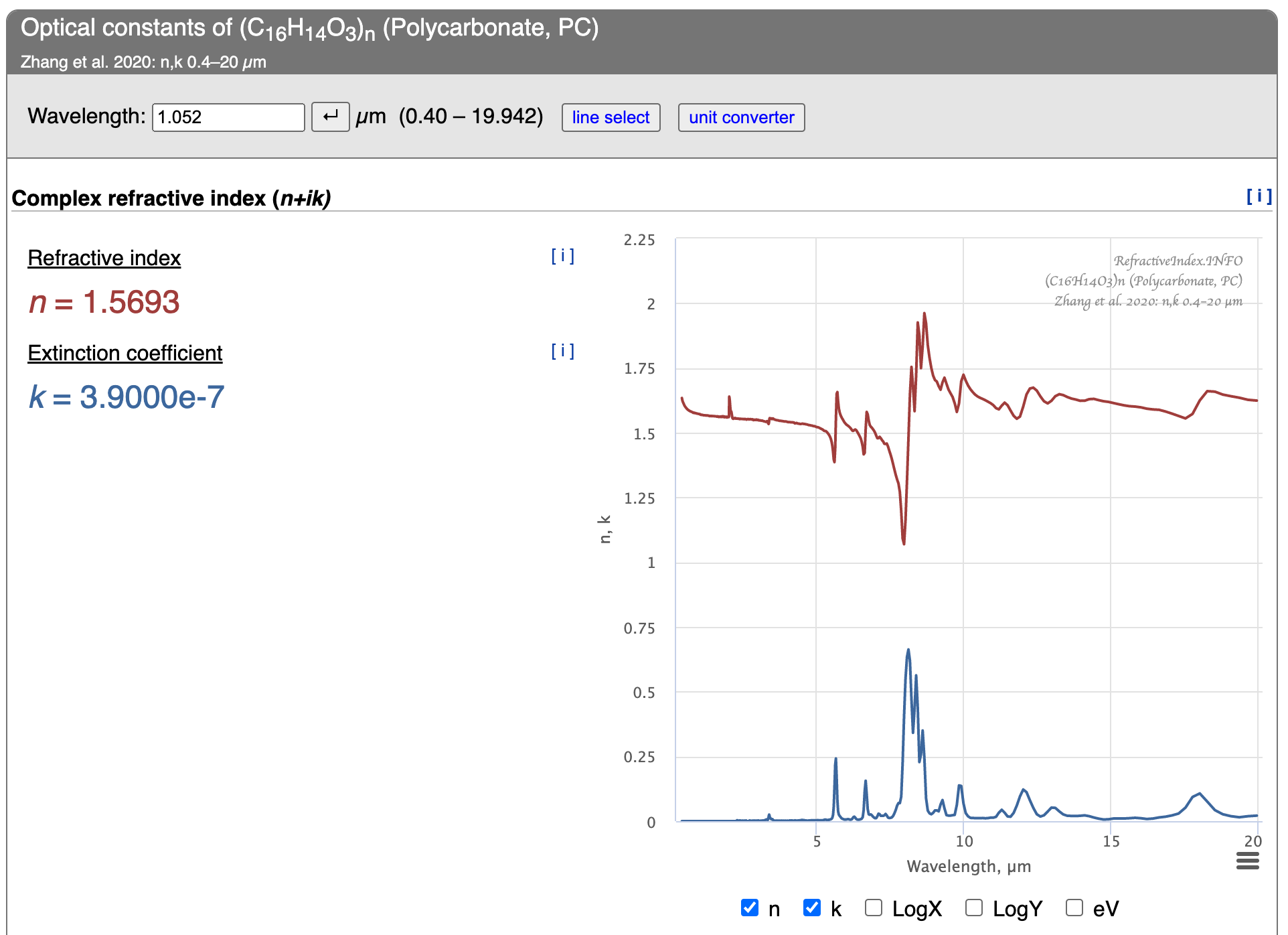
To get a link to the data for this material, scroll further down the webpage to the Data section:
Right mouse click on the Full database record link and choose the Copy Link Address menu item:
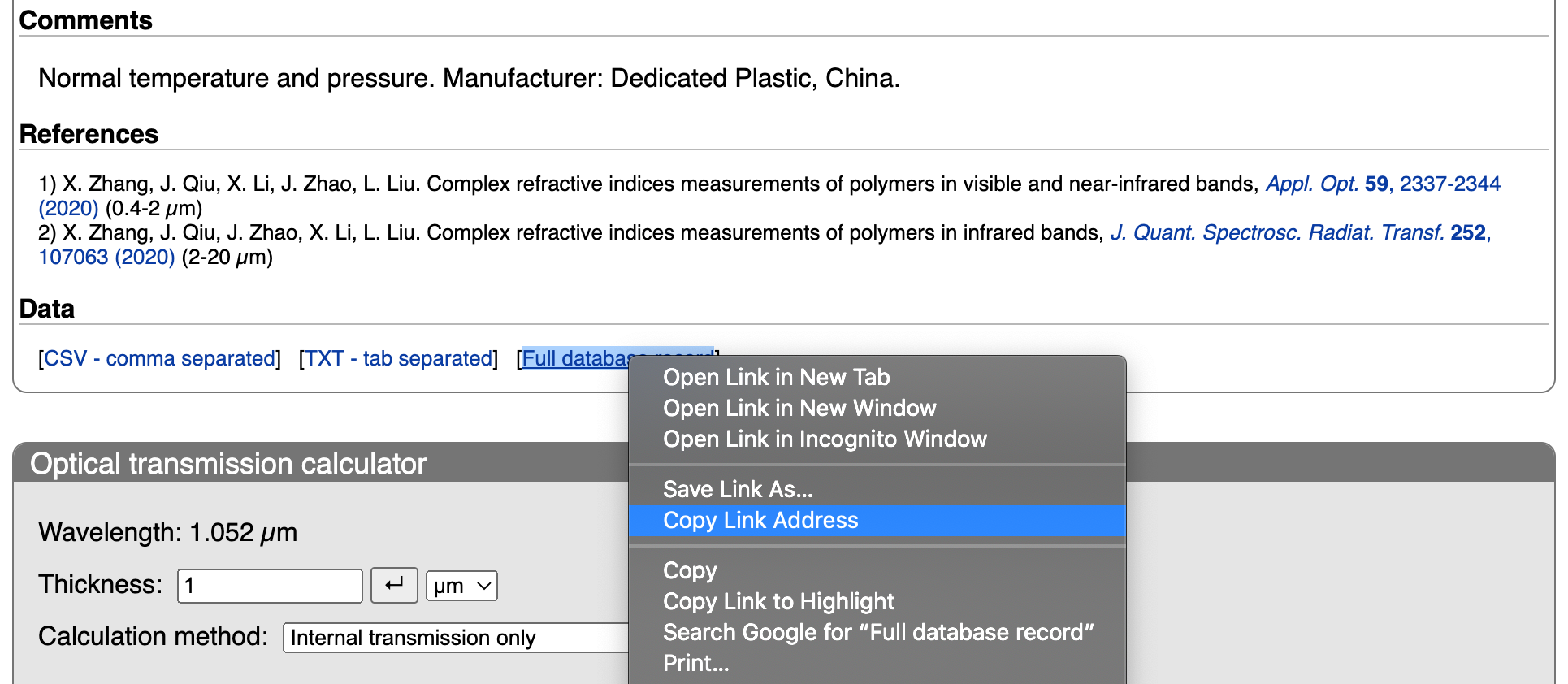
We can now define a variable for the polycarbonate data url and paste the link we obtained above into the right hand side of the definition.
polycarb_url = 'https://refractiveindex.info/database/data/organic/(C16H14O3)n%20-%20polycarbonate/Zhang.yml'
Use the read_rii_url() to import the material data into a python structure that reflects the original yaml formatted file. A suggested material name and catalog designation, based on the material url, are returned as well.
polycarb_yaml, name, catalog = rindexinfo.read_rii_url(polycarb_url)
The function create_material() takes the yaml definition of the material and the names and returns a glass instance.
polycarb = rindexinfo.create_material(polycarb_yaml, name, catalog)
The summary_plots() function can be used in a scripting environment to plot the (complex) refractive index data of a material.
summary_plots(polycarb, polycarb_yaml)
['tabulated nk']
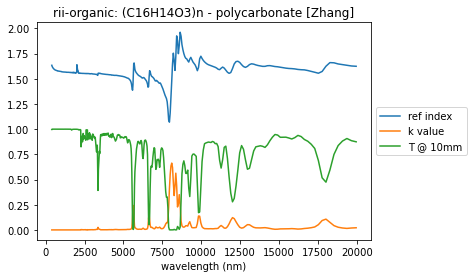
There is additional information available for each database entry, beyond refractive index and absorption. It is easiest to work directly with the imported yaml data.
polycarb_yaml.keys()
dict_keys(['REFERENCES', 'COMMENTS', 'DATA', 'SPECS'])
The ‘DATA’ key contains the raw index data. The ‘REFERENCES’ key is always present and documents the source of the data.
polycarb_yaml['REFERENCES']
'1) X. Zhang, J. Qiu, X. Li, J. Zhao, L. Liu. Complex refractive indices measurements of polymers in visible and near-infrared bands, <a href="https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.383831"><i>Appl. Opt.</i> <b>59</b>, 2337-2344 (2020)</a> (0.4-2 µm)<br>2) X. Zhang, J. Qiu, J. Zhao, X. Li, L. Liu. Complex refractive indices measurements of polymers in infrared bands, <a href="https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jqsrt.2020.107063"><i>J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf.</i> <b>252</b>, 107063 (2020)</a> (2-20 µm)'
The ‘COMMENTS’ key is often present with additional information. The ‘SPECS’ is a catch-all dictionary of additional data.
polycarb_yaml['COMMENTS']
'Normal temperature and pressure. Manufacturer: Dedicated Plastic, China.'
polycarb_yaml['SPECS']
{'n_absolute': True, 'wavelength_vacuum': False}
Material file examples
Below are a sampling of different material files of common interest.
SiO2
sio2_url = 'https://refractiveindex.info/database/data/main/SiO2/Malitson.yml'
sio2_yaml, name, catalog = rindexinfo.read_rii_url(sio2_url)
sio2 = rindexinfo.create_material(sio2_yaml, name, catalog)
summary_plots(sio2, sio2_yaml)
['formula 1']
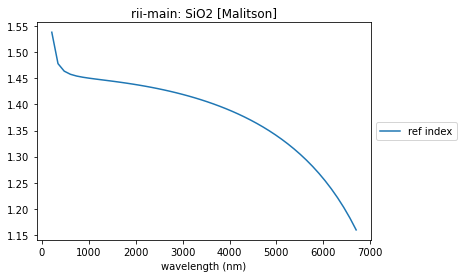
CaF2
caf2_url = 'https://refractiveindex.info/database/data/main/CaF2/Daimon-20.yml'
caf2_yaml, name, catalog = rindexinfo.read_rii_url(caf2_url)
caf2 = rindexinfo.create_material(caf2_yaml, name, catalog)
summary_plots(caf2, caf2_yaml)
['formula 2']
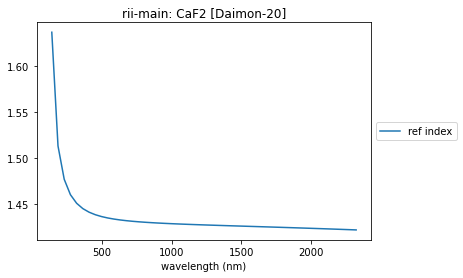
Germanium
ge_url = 'https://refractiveindex.info/database/data/main/Ge/Amotchkina.yml'
ge_yaml, name, catalog = rindexinfo.read_rii_url(ge_url)
ge = rindexinfo.create_material(ge_yaml, name, catalog)
summary_plots(ge, ge_yaml)
['tabulated nk']
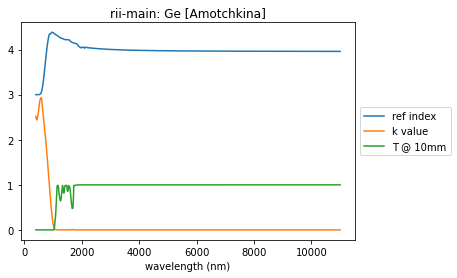
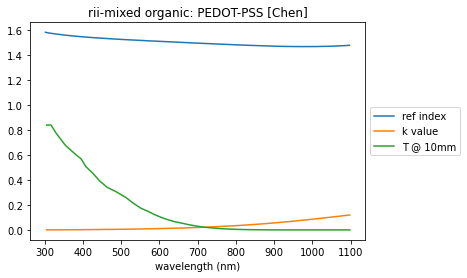
PEDOT
pedot_url = 'https://refractiveindex.info/database/data/other/mixed%20organic/PEDOT-PSS/Chen.yml'
pedot_yaml, name, catalog = rindexinfo.read_rii_url(pedot_url)
pedot = rindexinfo.create_material(pedot_yaml, name, catalog)
summary_plots(pedot, pedot_yaml)
['tabulated n', 'tabulated k']
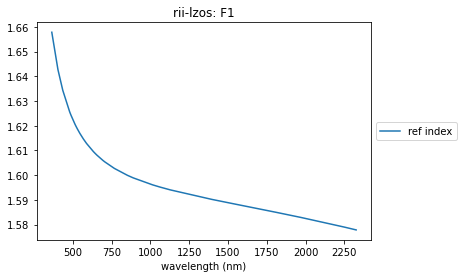
F1 LZOS
url = 'https://refractiveindex.info/database/data/glass/lzos/F1.yml'
F1_yaml, name, catalog = rindexinfo.read_rii_url(url)
F1 = rindexinfo.create_material(F1_yaml, name, catalog)
summary_plots(F1, F1_yaml)
['tabulated n']
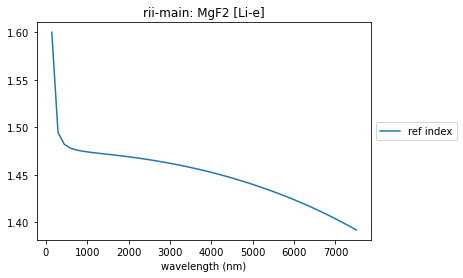
MgF2
url_root = 'https://refractiveindex.info/database/data/'
url = url_root + 'main/MgF2/Li-e.yml'
MgF2_yaml, name, catalog = rindexinfo.read_rii_url(url)
MgF2 = rindexinfo.create_material(MgF2_yaml, name, catalog)
summary_plots(MgF2, MgF2_yaml)
['formula 1']
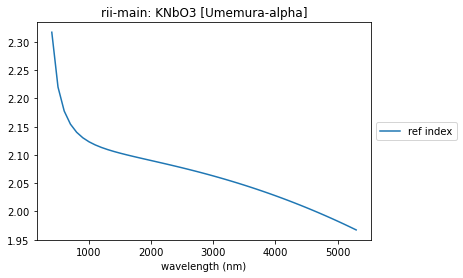
KNbO3
url = url_root + 'main/KNbO3/Umemura-alpha.yml'
KNbO3_yaml, name, catalog = rindexinfo.read_rii_url(url)
KNbO3 = rindexinfo.create_material(KNbO3_yaml, name, catalog)
summary_plots(KNbO3, KNbO3_yaml)
['formula 4']
KNbO3.data_range
array([0.4, 5.3])
KNbO3_yaml
{'REFERENCES': 'N. Umemura, K. Yoshida, and K. Kato. Phase-matching properties of KNbO<sub>3</sub> in the mid-infrared, <a href=" https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.38.000991"><i>Appl Opt.</i> <b>38</b>, 991-994 (1999)</a>',
'COMMENTS': 'n<sub>α</sub>; 22 °C.',
'DATA': [{'type': 'formula 4',
'wavelength_range': '0.40 5.3',
'coefficients': '4.4222 0.09972 0 0.05496 1 0 0 0 1 -0.01976 2'}]}
KNbO3.coefs
array([ 4.4222 , 0.09972, 0. , 0.05496, 1. , 0. ,
0. , 0. , 1. , -0.01976, 2. ])
len(KNbO3.coefs)
11